Understanding what is A1C and how to know if we're living a healthy life

The very first step is understanding what is a1c and how to measure it. A doctor needs to order an A1C test. Every adult should have this checked in mid life no matter if they have a hereditary predisposition to diabetes or not. Type-2 diabetes can always creep up if we don't watch our diet.

A Hemoglobin A1C test measures how much sugar is in your blood over an average of about three months.
This will let you and your doctor know where to begin so you can prevent the damage being done by diabetes.
What is a1c and how does it work?
Red blood cells travel all throughout your body. They give food and energy to your body.
They also remove toxins and carbon dioxide from your body and disposes of them.
Red blood cells live for about three months and then die while new cells are regenerated.
Hemoglobin attach to red blood cells and go for a ride
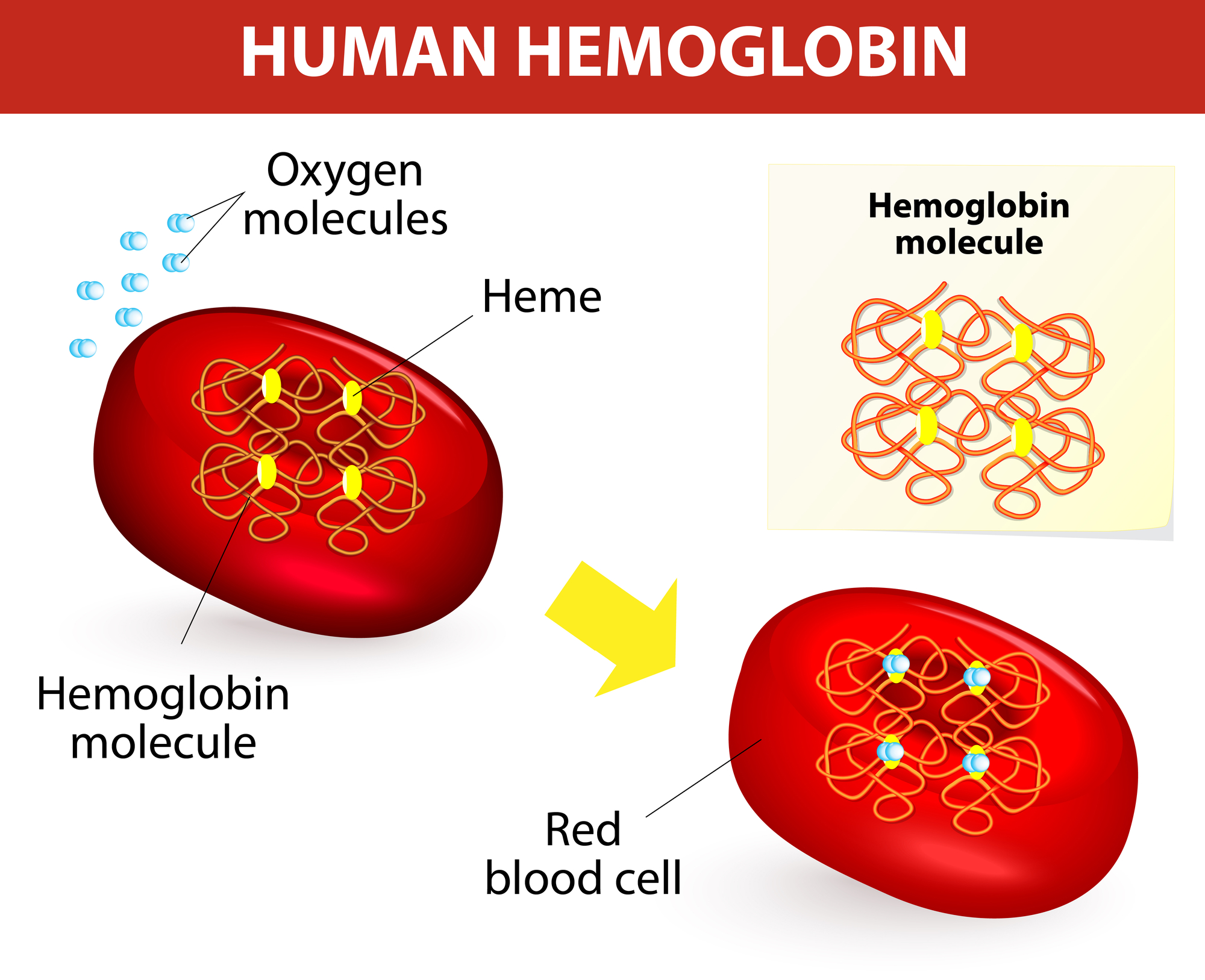
Hemoglobin gather up oxygen molecules and deliver them to all parts of your body.
You need hemoglobin molecules to be able to carry as much oxygen as possible.
Hemoglobin also carry glucose to deliver energy everywhere. It's important.
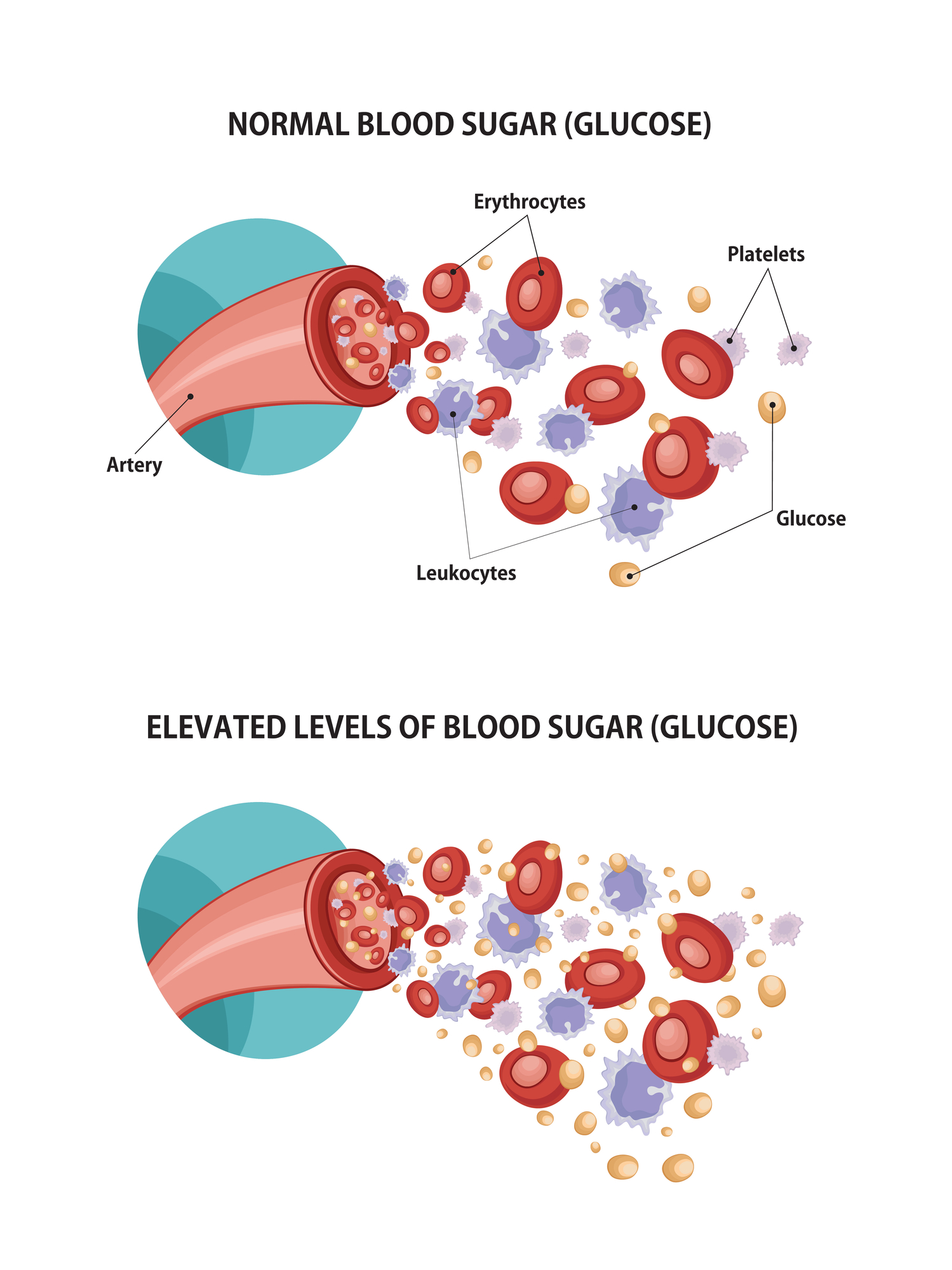
Your body needs energy so the hemoglobin carry oxygen and glucose throughout your body. A healthy glucose level in an A1C test shows that glucose is able to get into the cells and be used for energy. A normal level is about 5.7.
A high amount of glucose in the hemoglobin A1C test means something isn't working properly and the glucose isn't getting into the cells so it stays outside slowing down the hemoglobin needed for oxygen. An A1C of 6.5 and higher means diabetes.
An A1C of 5.8 to 6.4 is prediabetes. Time to take action.

Many people are prediabetic meaning they could develop type-2 diabetes if they don't monitor their diet and perhaps take preventive medicine.
There's a lot that can be done at this stage to slow down the progression of type-2 diabetes. There is valuable information at sites like MedlinePlus and the American Diabetes Association.
An A1C of 6.6 and higher means you are diabetic
It's really important to note that you can normally reduce this number with a proper diet. This also depends on how much damage has already been done. If you have been in the diabetic range for years, it will be more difficult to lower your A1C levels with diet alone.
If your doctor feels that you can't control your A1C numbers with diet alone, you may get prescribed a medicine like Metformin. This is usually in the early stages of diabetes or prediabetes. This can help glucose get into the cell instead of hanging outside of the cell waiting to get in. This will slow down the damage being done to your pancreas.
Your doctor may feel that a more aggressive and modern approach needs to be done. You may be prescribed something like Ozempic. A weekly injection that also helps the glucose get into the cell and lower overall A1C levels and help the pancreas function better.

If your pancreas has severe damage and it can't function without medication, you may be prescribed insulin. Insulin does the job of the pancreas and helps balance glucose levels. This may be a daily injection or even several injections daily. Insulin will help your body function better so the blood cells can deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
Another way to think about A1C levels
Your blood cells travel all throughout your body and they do it quite fast. They carry hemoglobin that is loaded up with oxygen and glucose to help us breath and have energy. For your body to have energy from glucose, it needs to get inside the cell and not latch onto the outside and just stay there until the cell dies. That slows down oxygen transfer.

Imagine that your hemoglobin cells are like a boat moving through the water.
Like unwanted barnacles attached to a boat, glucose is unusable outside the cell and it just slows things down.

If the glucose can't get inside the hemoglobin cell, it gathers on the outside.
The problem is that the oxygen needs that space on the outside of the cell to attach itself to. The cell is too crowded with glucose so the oxygen has to find a younger cell to attach to and that means less oxygen in the blood going where you need it to go.
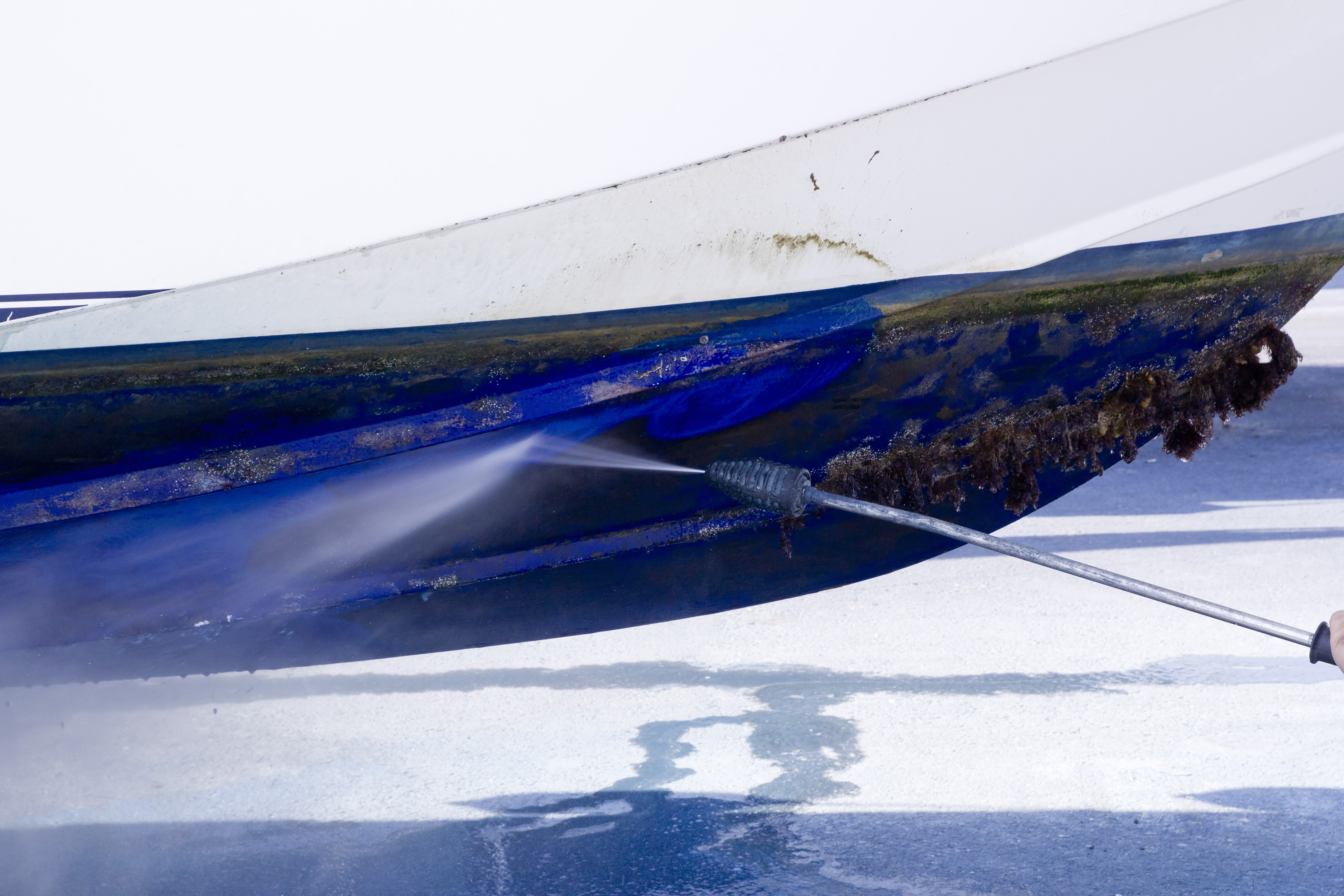

While this barnacle example is kind of a stretch to be similar to hemoglobin and glucose, it does show how a lack of maintenance of our bodies and diet can cause problems in the future. It's best to approach the problem when you can do a lot to prevent it from becoming much worse. Understanding what is A1C and how it affects your future health is a great step in the right direction to living a healthier, longer life.